
The Importance of Process Confirmation in a Lean Culture
Process confirmation is a cornerstone of Lean manufacturing, ensuring that processes operate as designed and deliver consistent results.

Why Manufacturers Hesitate to Invest in Operational Excellence
The paradox of manufacturers hesitating to invest in OpEx highlights the challenges of balancing risk, resources, and long-term planning.

How to Make 5S Stick
5S is more than just a tool for workplace organisation—it is a powerful driver of efficiency, safety, and employee engagement.

Internal Networking and Informal Communication in Operational Excellence
In any organisation, the flow of information is essential for achieving operational success. While formal structures and reporting lines are necessary, the reality is that much of the most valuable communication happens informally. These informal networks, based on trust and interpersonal connections, often operate outside the formal hierarchy but play a critical role in problem-solving, collaboration, and innovation.
Drawing inspiration from Dr Hannah Fry’s BBC Radio 4 programme The Gossip Mill, which explores how information flows through organisations, this article highlights the importance of understanding informal networks and how identifying key communicators can improve the way businesses operate.
What Are Informal Communication Networks?
Informal networks exist alongside the formal organisational structure, providing a more fluid way for employees to exchange information and ideas. Unlike formal communication, which follows a clear chain of command, informal communication moves across levels, departments, and teams in a more organic way.
In The Gossip Mill, Dr Fry discusses how a manufacturing company’s most trusted source of information wasn’t a senior manager but a Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) professional. This individual became the key point of contact for accurate information and advice, both formally and informally.
These networks are built on relationships and trust, and they can be highly effective in spreading useful information quickly. However, they can also be invisible, making them difficult to manage or leverage without careful observation.
The Role of Key Communication Nodes
Within any informal network, certain individuals emerge as key players. These “nodes” act as connectors, linking teams and departments, and ensuring that important information flows throughout the organisation.
Key nodes might not hold formal leadership positions, but their ability to influence others and their central role in informal communication often make them the linchpins of an organisation. For instance, in the example highlighted by Dr Fry, the HSE professional became a trusted figure who bridged gaps between different parts of the organisation.
Why Identifying Key Nodes Matters
- Keeping the Organisation Connected:
Key nodes often act as the glue that holds teams together, particularly during periods of growth, restructuring, or high turnover. Losing a key communicator can disrupt the flow of information and slow down decision-making. - Fostering Collaboration Across Teams:
By identifying and supporting key communicators, businesses can break down silos and encourage cross-team collaboration. These individuals are often uniquely positioned to share insights that improve processes and drive innovation. - Anticipating Bottlenecks:
Understanding how informal communication flows can help leaders identify potential weak points, such as teams or departments that are disconnected from the wider organisation. - Sustaining Organisational Culture:
Key communicators often play a significant role in shaping and maintaining company culture. They help reinforce shared values and norms through their everyday interactions.
Leadership’s Role in Supporting Informal Networks
- Recognising Informal Leaders:
It’s important for leaders to acknowledge and support those who play a key role in informal communication. These individuals might not hold senior positions, but their influence is invaluable. Simple actions, such as providing additional support, mentorship, or recognising their contributions, can strengthen their impact. In the example from The Gossip Mill, the organisation gave the HSE professional a promotion and a pay rise to formally recognise his role as a key communicator. This decision ensured that he could continue to act as a trusted source of information and support for the entire company. - Bridging the Gap Between Formal and Informal Structures:
While formal reporting lines are necessary, they can sometimes slow down decision-making or limit collaboration. Leaders who recognise the value of informal networks can encourage open communication across both formal and informal channels, making the organisation more agile and responsive. - Encouraging Open Communication:
Leaders have a responsibility to ensure that informal networks are inclusive and that information flows freely across the organisation. This prevents information silos and ensures that everyone has access to the knowledge they need to succeed.
Informal Networks and Customer Success
Understanding internal networks doesn’t just benefit employees—it also has a direct impact on customers.
- Faster Response Times:
When informal networks are strong, employees can quickly connect the right people to solve customer problems. This reduces delays and ensures a smoother customer experience. - Better Insights for Customer Service:
Key communicators often hold deep knowledge about customer needs and challenges. By supporting these individuals, businesses can ensure that customer-facing teams are well-informed and equipped to deliver the best possible service. - Innovation That Benefits Customers:
Informal networks encourage the exchange of ideas between employees from different areas of the business. This can lead to innovations in products, services, or processes that directly enhance the customer experience.
Wrapping Up
Informal communication networks are often overlooked, but they are critical to the success of any organisation. By identifying and supporting key communicators, businesses can improve the flow of information, foster collaboration, and create a more agile and innovative environment. Leaders play a vital role in nurturing these networks, ensuring that they align with organisational goals and values.
In a fast-changing business world, mastering informal communication is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for staying competitive and meeting customer expectations.
If you want to learn more about how internal networks can enhance your organisation’s performance, contact us at Project7 Consultancy. Let’s discuss how our tailored 3P process can help you unlock your operational excellence potential.

How to Successfully Integrate Veterans into Your Business
The British Armed Forces instil discipline, resilience, and a strong commitment to achieving goals, even under challenging conditions. Each year, over 15,000 personnel transition from military to civilian life, offering a valuable talent pool for British businesses. Veterans bring unique skills and qualities that can greatly benefit civilian workplaces, but ensuring they “hit the ground running” requires a tailored onboarding process.
This guide outlines best practices for integrating veterans and offers insights applicable to onboarding all new employees, creating an effective and inclusive induction process that supports both personal and business growth.
Recognising the Value of Veterans
Veterans possess skills that often go beyond traditional qualifications—leadership, teamwork, problem-solving, and decision-making under pressure. Many have experience in logistics, project management, engineering, IT, and HR, roles that overlap significantly with civilian business needs. Beyond technical skills, veterans also bring qualities like responsibility, emotional intelligence, and a results-driven mindset.
To maximise their potential, businesses must recognise these transferable skills. With an effective orientation process, the wealth of experience gained in military service can be smoothly transitioned into civilian roles.
Best Practices for Integrating Veterans into Your Business
- Create Job Adverts with Intention
Attracting veterans starts with writing job adverts that resonate with their values and skills. Use clear, concise language to highlight qualities like leadership, discipline, and adaptability. Emphasise how these attributes are valued in your company and align with its culture. Mention your commitment to integrity, teamwork, and professional growth, and encourage veteran applicants. This demonstrates that their background is valued and that they have a place in your organisation. - Recognise and Translate Transferable Skills
Military veterans possess skills that may not always align with conventional qualifications but are highly applicable to business needs. For instance, a logistics officer in the armed forces may not have specific supply chain credentials but has extensive experience managing complex resources in high-pressure environments. Educate hiring managers on how military experience translates into business roles. Partnering with veteran organisations, such as The Royal British Legion, can help identify and translate military skills into business contexts before veterans start their new roles. - Develop Tailored Onboarding Programmes
A personalised onboarding process is key to veterans’ success. This process should acknowledge their military background while bridging gaps between military and civilian work cultures. Veterans often thrive in structured, goal-oriented environments, making a clear induction process essential. An effective onboarding programme should include:
– Structured Induction: Outline the company’s mission, values, and goals, showing veterans how their role contributes to the bigger picture.
– Mentorship: Pair veterans with mentors, ideally other veterans who have successfully transitioned to civilian roles, providing guidance and support during the adjustment period.
– Cultural Adaptation: Help veterans understand civilian work culture nuances, such as lateral communication and collaborative decision-making, which may differ from the military structure. - Leverage Veterans’ Leadership Abilities
Veterans bring proven leadership skills, making them ideal candidates for supervisory or managerial roles. Their experience in leading teams and ensuring mission success transfers effectively to both middle management and senior roles. Early leadership roles allow veterans to demonstrate their ability to guide others and drive projects, creating immediate value for your organisation. Their capacity to foster teamwork and implement processes makes them well-suited to roles requiring leadership and accountability. - Invest in Ongoing Professional Development
Providing ongoing professional development is essential for veterans’ long-term growth. Invest in industry-specific training, certifications, or leadership programmes to help veterans expand their skill set. This commitment aligns with veterans’ desire for career progression and helps build a mutually beneficial relationship. By offering growth opportunities, businesses can benefit from a motivated, loyal, and continuously improving workforce.
Applying Veteran-Oriented Practices to All New
EmployeesThe strategies for onboarding veterans are equally valuable for onboarding all new hires, creating an inclusive and effective induction process:
- Structured Induction: A clear onboarding programme helps all employees understand how their work contributes to the business.
- Mentorship Programmes: Mentors can guide new employees and ease their transition into the company culture.
- Leadership Development: Nurturing leadership potential from day one helps develop a motivated, goal-driven team.
- Focus on Growth: Providing training and development opportunities keeps employees engaged and benefits retention and satisfaction.
Conclusion: A Win-Win for Businesses and VeteransIntegrating veterans into civilian businesses is not just about corporate social responsibility—it’s a strategic decision that brings real value. Veterans are skilled, adaptable, and bring an exceptional work ethic. By recognising their transferable skills, providing tailored onboarding, and offering professional development, companies can unlock veterans’ full potential.
These best practices also benefit all employees, fostering a supportive, growth-oriented culture. Whether military or civilian, every employee can thrive with a structured, inclusive induction process that sets them up for success.

Want to Get the Edge on your Competitors – Hire a Veteran
Whether it be industry, commerce or retail, every business in the UK is looking at how to gain the edge over their competitors in a market where trained and motivated personnel are becoming harder and harder to find. Many businesses have recreated apprenticeship schemes, and they are to be applauded. However, if you need trained high-calibre people today who master cutting-edge technology in highly complex, high-pressure environments, then look to an often-overlooked talent pool that can provide this edge – military veterans. In the United Kingdom, there is a growing recognition of the skills, values, and attributes that ex-service personnel bring to the civilian workforce. Veterans have been trained to manage ambiguity and high-pressure situations, work as part of a team, lead with authority, and adapt quickly to ever changing environments. By adding a focus on hiring veterans, UK industries can tap into a rich resource of skilled individuals who possess qualities that are difficult to cultivate outside of military service. With National Remembrance Day on the horizon once again, let’s look at what each of us can do to hire a hero.
Transferable Skills and Expertise
Military veterans are equipped with a diverse skill set that can easily be transferred to civilian industries. Whether it’s leadership, problem-solving, project management, or technical skills, veterans are often trained in roles that mirror those in the business world. For example, a logistics officer in the military is responsible for supply chain management, ensuring timely delivery of goods and resources. These same skills are invaluable in sectors such as retail, manufacturing, or distribution. When I retired from the RAF as an aerospace engineer, my transferable skills were immediately recognised to become the reliability engineer in a major paper manufacturing plant.
One real-world example of a company with a veteran focus is Amazon UK, Military Programs | Amazon.jobs which has actively recruited veterans to fill roles in its logistics and operations teams. An example they quote is of a former Army logistics officer, transitioning into a management role at Amazon. He credits his military experience with giving him the ability to manage teams, plan complex operations, and meet critical deadlines—skills that are directly applicable to his civilian role.
Moreover, many veterans possess specialised technical skills, such as in IT, engineering, and cybersecurity. The UK’s technology sector, which is experiencing rapid growth, can benefit greatly from veterans who have received cutting-edge and often unique training in these areas. The Defence and Security Accelerator (DASA) Defence and Security Accelerator – GOV.UK (www.gov.uk) has demonstrated the power of veteran expertise in cybersecurity, working with veterans to help tackle issues related to national security and cyber threats. Their military training allows them to think critically, operate under pressure, and make informed decisions quickly—qualities that are essential in the tech world.
Leadership and Teamwork
Leadership is a cornerstone of military service. Veterans are used to being thrust into complex leadership roles early in their careers, managing teams, motivating people, and leading by example under challenging circumstances. For example, I went from being an Engineering Squadron Commander to the NATO spokesperson in the Kosovo war in less than a week. These leadership experiences translate well into management and executive positions in the corporate world. Furthermore, military personnel are skilled in teamwork and understand the importance of collaboration, communication, and shared responsibility.
For example, Jaguar Land Rover (JLR), one of the UK’s largest car manufacturers, has launched a programme specifically aimed at hiring veterans with the aim of becoming the ‘employer of choice’ for veterans as they leave the military Armed Forces Engagement | JLR Corporate Website (jaguarlandrover.com). Recognising the leadership qualities veterans bring, JLR recruits ex-service personnel to manage teams and lead projects. Veterans at JLR have thrived, particularly in engineering and production, where leadership, attention to detail, and effective communication are critical. Veterans understand how to achieve objectives through effective team dynamics, contributing significantly to the company’s overall efficiency.
Resilience and Adaptability
One of the most valuable qualities veterans bring to the workforce is resilience. Military service often involves dealing with high-pressure situations, uncertainty, and rapidly changing conditions. Veterans are trained to remain calm under pressure, think clearly, and make critical decisions. This ability to manage stress and adapt to new challenges is crucial in many industries, especially those that require crisis management or rapid problem-solving, such as healthcare, finance, or construction.
In the UK construction sector, Balfour Beatty Armed Forces (balfourbeatty.com) has successfully integrated veterans into their workforce. Veterans have been able to apply their experience in crisis management and adaptability to the often unpredictable world of construction projects. Their ability to manage complex, high-pressure situations makes them valuable employees in roles that require quick thinking and effective decision-making.
Strong Work Ethic and Commitment
Veterans are instilled with an intense sense of duty and commitment, which makes them highly motivated and dedicated employees. They understand the importance of perseverance, discipline, and seeing a task through to completion. These traits are essential in the private sector, where businesses need employees who are not only skilled but also driven to succeed and deliver results.
Take Barclays, 10 years of Barclays Military and Veterans Outreach | Impact | Barclays (home.barclays) for instance, which has a robust program for hiring and supporting veterans. Barclays recognises the value veterans bring in terms of dedication and commitment to their roles. Veterans working at Barclays have excelled in positions ranging from customer service to high-level management, where their military work ethic has shone through. In industries such as finance, where attention to detail, commitment to compliance, and customer satisfaction are paramount, veterans have been able to excel due to their work ethic and dedication to detail.
Diversity and Inclusion
Hiring veterans also promotes diversity and inclusion within the workforce. Veterans come from a wide variety of backgrounds, and their experiences in the military give them unique perspectives that can enrich a company’s culture. Bringing people into the workforce who have lived and worked in diverse environments encourages innovation and fosters an inclusive atmosphere. Veterans are also accustomed to collaborating with people from diverse backgrounds cultures and languages and will help create a more cohesive and collaborative workplace.
FDM Group, Ex Forces Careers & Recruitment | FDM Group UK a UK-based technology services company, actively recruits veterans as part of their commitment to diversity and inclusion. Veterans have brought fresh perspectives to FDM’s work in IT and business consulting, leading to innovative solutions and a more dynamic workplace environment. The company’s veteran employees have proven adept at working in multicultural teams and tackling complex global projects with a fresh outlook.
Loyalty and Retention
Employee retention is a major challenge for many businesses, with high turnover rates leading to increased costs and lost productivity. Veterans tend to be loyal employees, often remaining with companies longer than the average civilian worker. In my own case, I spent 30 years in the RAF and had more than 15 addresses so now look for stability in my civilian life. So veterans are accustomed to long-term commitment and understand the importance of loyalty and stability in their second careers.
Companies such as Capita, Military service leavers | Opportunities for veterans | Capita a UK outsourcing and professional services firm, have noticed higher retention rates among their veteran employees. By providing veterans with meaningful roles that align with their skills, Capita has been able to foster a sense of belonging and commitment, which has translated into lower turnover rates and higher job satisfaction among veterans.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Public Image
Finally, employing veterans is not just good for business; it’s also good for a company’s reputation. Many businesses are now prioritizing corporate social responsibility (CSR) and Industry 5.0, and hiring veterans can form a key part of this strategy. By supporting ex-military personnel, companies can enhance their public image and demonstrate a commitment to ethical values such as in giving back to society. This not only appeals to customers and stakeholders but also boosts employee morale, as workers appreciate being part of a socially responsible organisation.
The National Grid, Military service leavers | Opportunities for veterans | Capita one of the UK’s largest utilities companies, has taken a lead in this area, setting up programmes specifically to help veterans transition into civilian roles. By showcasing their efforts in supporting ex-service personnel, National Grid has strengthened its reputation as a socially responsible company while benefiting from the expertise veterans bring to their workforce.
Conclusion
The benefits of employing military veterans in the UK are clear. Veterans bring transferable skills, strong leadership, resilience, adaptability, a strong work ethic, and a commitment to diversity and inclusion. Their loyalty and dedication can also help reduce employee turnover and enhance a company’s public image through corporate social responsibility initiatives. As more UK industries recognise the value veterans provide, they will be able to tap into a rich and underutilised talent pool, ensuring their long-term success while supporting those who have served the country.
By focusing on employing more veterans, UK businesses can benefit from a workforce that is trained, disciplined, and ready to take on the challenges of today’s dynamic industries. If you are looking for a readily available pool of trained and motivated people, hire a veteran.

Building Operational Excellence into Factory Moves
Relocating or expanding a manufacturing facility is a complex, capital-intensive endeavour that can either enhance operational efficiency or lock-in costly inefficiencies. By embedding operational excellence principles, particularly those drawn from Lean methodologies into factory moves you will unlock strategic opportunities to improve productivity, reduce waste, and build a sustainable culture of continuous improvement.
In our almost 20 years-experience, we have often been called into established manufacturing plants to unlock new potential due to sometimes decades old poor design. This article explores the advantages of building operational excellence into factory moves from the outset in order that you can maximise throughput and profitability from day one.
Preventing In-Built Inefficiencies Through Lean Principles
A factory relocation or expansion involves critical phases, including design, layout planning, equipment selection, workforce training and design of standard operating procedures. Each of these stages offers an opportunity to embed operational excellence through Lean thinking. Here we will expand on each of those phases and show you how to avoid built-in inefficiency.
Lean Thinking in Layout Design
A core element of Lean manufacturing is the focus on optimising flow—whether it’s materials, information, or people. During a factory move, using Lean principles to design the plant layout is critical. Our experience shows that factories that don’t integrate Lean thinking often suffer from:
- Excessive transportation between workstations.
- Overproduction due to poor material handling.
- Long lead times because of inefficient process flows.
- Extra cost when leadership realise, they have poor flow and ‘bottlenecks’ and have to shut the plant down for a costly re-engineering exercise.
- Excess Work In Progress when isolated workstations are only focused on their individual output rather than the entire process output.
- Poor Customer Relationships when the supply chain is interrupted causing them to look for future multiple suppliers rather than building on their relationship with you.
By applying Lean tools such as Value Stream Mapping (VSM) and Bottleneck Analysis before the move, you will identify and eliminate non-value-added activities, ensuring that the new facility promotes a smooth and balanced flow of work. Strategic positioning of machinery and workstations, designed to minimise unnecessary movement and queues, will significantly boost your plant efficiency from Day 1.
Cultural Integration: A Foundation for Sustained Improvement
A successful factory move isn’t just about relocating physical assets; it requires a parallel investment in cultural transformation. The Project7 Consultancy 3P model (focuses on People + Process = Performance. We have repeatedly shown how investing in these three essential threads will maximise your relocation or workflow optimisation and sustain your business success. These three also build a culture of continuous improvement (Kaizen), which emphasises the importance of culture in sustaining operational excellence.
Establishing a Lean Culture Early
Culture change must be a strategic priority well before the physical relocation or re-organisation occurs. Involving employees from the beginning whilst nurturing psychological safety and emotional intelligence, fosters engagement, ownership and embeds a mindset of continuous improvement. Early buy-in from an engaged workforce allows teams to identify operational pain points and contribute to solutions. This is especially important in avoiding the reintroduction of inefficient practices post move. As a bonus, engagement and ownership foster sustainment, which is essential for you new plant.
- Kaizen mindset: Encourage employees to actively participate in continuous improvement initiatives and problem solving throughout the move.
- Leadership by example: Leadership needs to embody and model Lean principles and set expectations for continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Embedding a culture of operational excellence pre-move leads to sustained efficiency gains post-move. Without this cultural groundwork, companies risk the common pitfall of installing efficient systems without the commitment or discipline from the work force to sustain them.

The P7 Way: A Blueprint for Long-Term Success
The Toyota Way has long been recognised as a gold standard for operational excellence. However, the reason it worked so well for Toyota is that it was built into their culture and their way of working. For your business to have an effective Lean continuous improvement culture that works for you, you need a process that takes the tools of Lean and adapts them to your culture and your way of working. That is where the Project7, 3P model comes into its own, and why its success has been replicated across industry. The 3P model is rooted in long-term thinking, problem-solving, and respect for people and offers invaluable guidance for companies undertaking factory moves.
Long-Term Thinking Over Short-Term Gains
The Project7 3P model encourages a focus on the long term. In the context of a factory move, this mindset ensures that immediate cost-saving decisions (e.g., opting for cheaper machinery or cutting corners in layout planning) do not compromise long term operational efficiency.
Investing in Lean technology, automating waste-reducing processes, and fostering a culture of problem-solving might incur upfront costs, but they pay dividends over time. The 3P model’s emphasis on long-term success ensures that even after the move, the company is well-positioned to adapt and improve its processes continuously.
Problem-Solving and Root Cause Analysis
A core aspect of the Project7 3P model is its emphasis on problem-solving through root cause analysis in participative action teams. Integrating this approach during a factory move allows teams to address potential systemic inefficiencies before they become embedded in the new facility.
For example, when deciding on the placement of machinery or the layout of workstations, asking “Why?” repeatedly, with those who will have to own the process, can reveal deeper insights into workflow inefficiencies, ensuring that decisions are made with operational excellence in mind. Solving these issues at the planning stage is far more cost-effective than addressing them after the factory is operational.
Key Operational Excellence Tools to Apply in Factory Moves
Several Lean tools and practices are particularly relevant to factory moves. When applied from the outset, they help ensure that operational excellence is built into the new facility:
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM): Visualises the entire process, identifying waste, and non-value-adding activities.
- Workplace Organisation (5S): Organises the workspace for efficiency by ensuring a clean, organised, and safe environment, minimising wasted time searching for tools and materials.
- Kanban and Just-in-Time (JIT): Ensures materials and parts are available at the point of need whilst reducing inventory costs and preventing overproduction.
- Standard Work: Ensures that the best practices and processes are standardised, reducing variation and ensuring consistency in output.
- Process Conformation: Ensures that the agreed processes are being maintained to ensure variation is not being reintroduced.
By using these and other Lean tools during the planning and implementation phases of a factory move, manufacturers can significantly reduce inefficiencies and set the foundation for operational excellence in the new facility from day 1, rather than having to reengineer them at a later date.
Conclusion
Factory relocations or expansions represent a pivotal moment in a company’s journey. By embedding operational excellence and Lean principles into the move from the outset, manufacturers can avoid the common pitfalls that we so often see when called into to re-engineer a struggling or failing plant, factory, or shop floor workflow. Drawing on the Project7 3P Model way of long-term thinking, problem-solving ethos, and cultural emphasis, organisations can create an environment where continuous improvement thrives.
In doing so, we find that businesses not only avoid in-built inefficiencies but also position themselves for sustained growth and success in an increasingly competitive market. The journey to operational excellence should begin long before the first machine is installed—by embedding these principles we discuss above into every decision, companies can ensure that their new facility is a model of efficiency, adaptability, and performance.
For more information on how similar strategies can benefit your organisation, feel free to reach out to us.
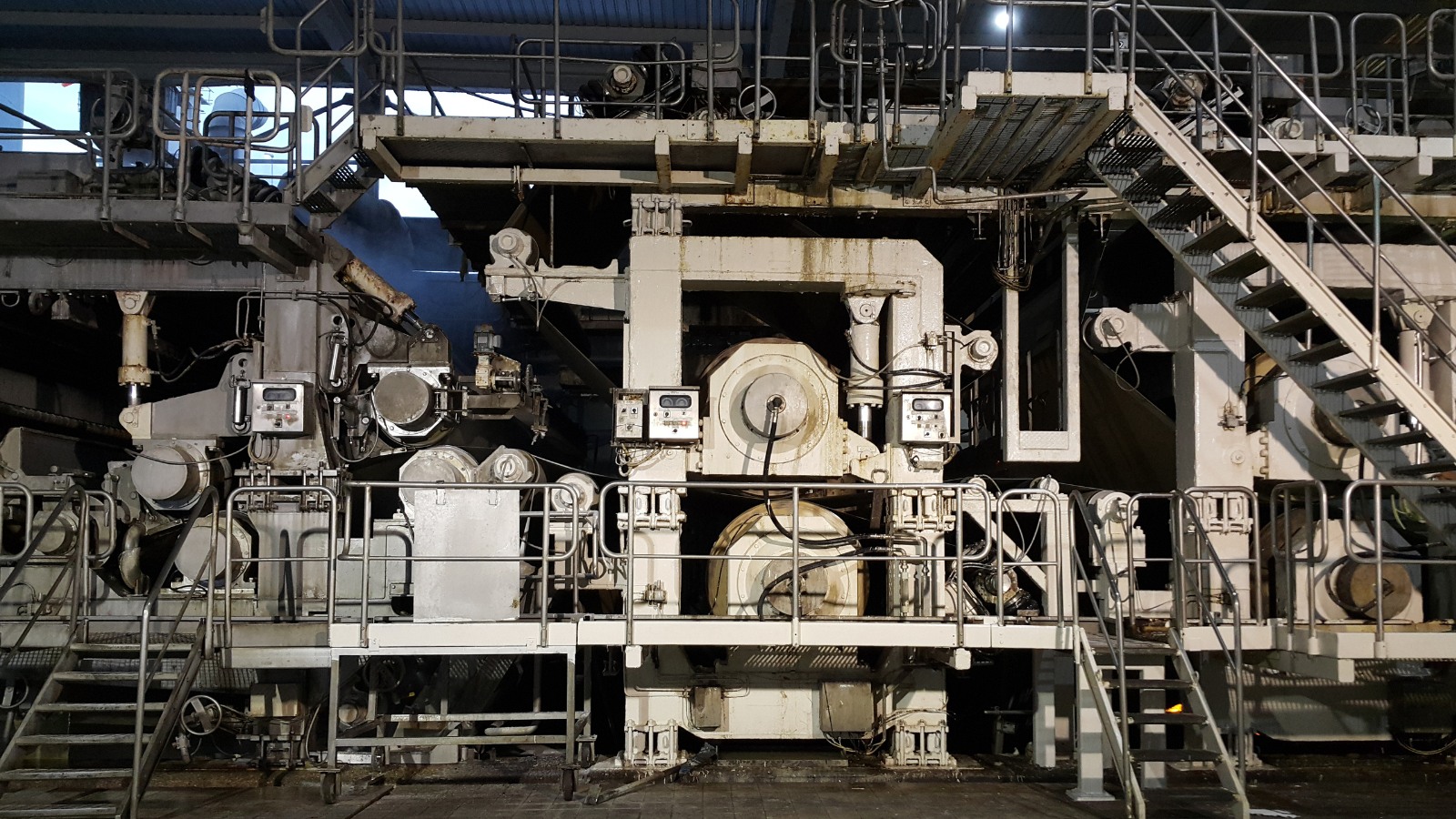
Reflecting on Our Hydra-Purge Throughput Improvement Project
Solving persistent operational issues requires a structured, data-driven approach. In one of our previous projects, we tackled a long-standing issue with a Hydra-Purge system at a paper production facility. The system had consistently been blanking over during maximum production, particularly when handling heavier paper grades, severely affecting throughput. Despite efforts to resolve it, the root cause had remained undetected for over five years.
Operations initially believed the problem lay with incorrect settings between the extraction plate and the impeller. At maximum capacity, the Hydra-Purge would stop functioning, causing pulp flow to drop to zero. Using Six Sigma DMAIC principles, we took a data-led approach to investigate and identify the root cause.
When operations inspected the system during the next occurrence of zero flow, they found it clean, ruling out the original assumption of blanking over. This prompted a deeper analysis of the process. We assembled a team, including the Plant Chief Engineer, the Hydra-Purge OEM, the process engineer, the Operations Manager, and the wet-end operator, to review the data.
On further examination, we discovered that the feed to the Hydra-Purge was being starved during maximum production. The issue was traced to a weir plate that hadn’t been cut low enough, restricting the pulp flow from the pulper to the Hydra-Purge at peak demand.
The solution was straightforward: lower the weir plate to allow sufficient pulp flow. This low-cost modification resolved the problem after more than five years of production issues.
The impact was immediate. The problem was solved in just three days, throughput improved instantly, and the modification boosted production to record levels, adding the equivalent of an extra shift of production time per month.
This project demonstrates the power of focused leadership, data analysis, and collaboration. By questioning assumptions and thoroughly analysing process data, long-standing operational issues can be solved, unlocking new levels of performance.
For more information on how similar strategies can benefit your organisation, feel free to reach out to us.

Problem Solvers and Decision Makers as Drivers of Lean Culture
It is well established that Lean cultures can only be successful when all team members become problem solvers and decision-makers. However, the reality of creating such high-performance teams and individuals is consistently underestimated. So, what does it take to transform a group of individuals into a cohesive team of decision-makers and problem solvers? Building on 30 years of military leadership experience and 15 years of industrial leadership and consulting experience, we will highlight some of the characteristics critical to nurturing groups of individuals to become high-performance problem solvers and decision-makers.
Critical Characteristics
Establish Clear Goals and Objectives
When team members understand and commit to the same objectives and goals, they align their efforts and make decisions that support these objectives and goals. Goal alignment seemed easier in the military than in civilian practice. Even when the business ‘mission and vision’ is proudly exhibited on a poster in reception, civilian processes can be stymied by self-interest, hidden agendas, and poor decisions based on short-termism. Successful implementations of Lean by companies such as Toyota, Airbus, Rolls Royce, and Procter & Gamble operate at a maturity level more akin to the military. They cut through local politics, rise above the average, and have decision-makers operating from the bottom up when it comes to problem-solving, decision-making, and ownership.
Effective Communication
Open and transparent communication is critical. Team members need to share information, listen actively, and provide constructive feedback. Here, the Lean tools of Genba, Visual Management, RCPS, and process confirmation promote communication. These tools, essentially leadership practices in the military, foster mutual understanding and help in making informed decisions as leaders and teams follow the most current information to make the best decisions.
Defined Roles and Responsibilities
Clarifying each team member’s role and responsibilities helps prevent overlap and confusion. When individuals know their specific contributions to the team’s goals, they can focus on their tasks and make decisions pertinent to their areas of responsibility. This should include practised SOPs, one-point lessons, SMED schedules, and detailed TPM work orders.
Trust and Mutual Respect
Trust among team members is the foundation of effective teamwork. When individuals trust and respect each other, they are more likely to share ideas, take risks, and support one another’s decisions. That trust is built on competence and character and is the foundation of authentic leadership, respect, humility, psychological safety, and emotional intelligence.
Psychological Safety
Psychological safety plays a critical role in team decision-making by fostering an environment where members feel comfortable expressing their thoughts, ideas, and concerns without fear of ridicule or retribution. This openness encourages diverse viewpoints and constructive dialogue, leading to more thorough and innovative problem-solving. When team members trust that their contributions are valued and respected, they are more likely to engage actively, take risks, and collaborate effectively, ultimately enhancing the quality and effectiveness of decisions made by the team.
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence (EI) significantly enhances team decision-making by enabling members to navigate interpersonal dynamics with empathy, self-awareness, and effective communication. High EI allows team members to understand and manage their own emotions and recognise and influence the emotions of others, leading to improved collaboration and conflict resolution. By fostering a supportive and empathetic environment, emotionally intelligent teams can better leverage diverse perspectives, address issues constructively, and make decisions that consider both the logical and emotional aspects of a situation. In practice, this means leaders must get out of the office, interact, and build relationships with all their people. Leaders cannot lead those whom they do not know.
Collaborative Climate
A positive and collaborative team climate encourages members to work together harmoniously. This involves fostering a sense of belonging, encouraging cooperation, consciously building trust, and valuing diverse perspectives. It also means avoiding hidden agendas. In the military, frequent postings necessitated immediate collaboration when joining a new team. While the rank system helped, sustained collaboration depended on leaders walking the walk.
Decision-Making Processes
Establishing clear and efficient decision-making processes ensures that the team can make timely and well-considered decisions. This includes defining how decisions will be made, who will be involved, and how conflicts will be resolved. Sustaining these processes as cultural norms is critical. Choose a process that meets the complexity of the problem and stick with it. Reinventing the wheel with each decision-making process is inefficient and only sustains chaos.
Leadership and Guidance
Effective leadership is critical for steering the team in problem-solving until the team is ready to take on the responsibility of problem-solving themselves. Leaders should facilitate discussions, encourage participation, and provide direction while empowering team members to take ownership of their decisions.
Diversity and Inclusion
A diverse team brings a variety of perspectives and experiences, which can enhance decision-making. Inclusive practices ensure that all voices are heard and considered, leading to more comprehensive and innovative solutions. In one particularly difficult engineering problem, bringing in an HR professional and a receptionist provided considerable insight that complemented the usual engineering-focused thinking.
Conflict Resolution Skills
Conflict is not unusual when developing and nurturing teams. However, developing skills to manage and resolve conflicts constructively ensures that disagreements do not hinder the team’s progress but instead can lead to better decision-making.
Continuous Improvement
A commitment to continuous improvement helps teams to reflect on their processes and outcomes, learn from their experiences, and make necessary adjustments to enhance their effectiveness. Enable the team to set aside time to learn from their experiences and build their expertise or live with lost opportunity.
Wrapping Up
We have detailed the critical characteristics that will enable you to nurture your teams to become decision-makers and problem solvers. Now comes the tough part: the path of change.
In our next article, we will detail how you can nurture your people through the complex path of change, teach you about change readiness, how to avoid change fatigue, and how to be successful by following the RESPECT© change program.

Reflecting on our Practical Problem Solving and Kata Coaching Project
One of the major outcomes of a Project7 engagement is to empower organisations with the tools and methodologies needed for continuous improvement. One of our significant previous projects involved enhancing the problem-solving capabilities of a major manufacturing facility. This reflection explores the challenges faced, solutions implemented, and the impactful outcomes achieved through practical problem-solving and Kata coaching.
Our client is a leading provider of secure products and services, operating across 24 global locations with a workforce of 3,230 employees. One of their key manufacturing sites, responsible for producing a significant portion of the company’s output, had been facing issues with problem-solving. Despite having an in-house Operational Excellence framework that delivered several improvements over three years, the site struggled with a lack of a defined approach to problem-solving, leading to recurring issues and inefficiencies.
The primary challenge was the absence of a standardised methodology for problem-solving, resulting in shallow solutions such as firefighting and troubleshooting rather than addressing root causes. This lack of a systematic approach led to repeat occurrences of problems and impacted quality and cost metrics. Additionally, there was no leadership coaching capability in place to support problem management. Approaches to problem-solving were more directive than questioning, leading to a lack of learning and understanding.
To address these challenges, Project7 engaged with the site’s leadership team to develop and integrate a practical problem-solving system and methodology. This involved “Improvement Kata” coaching to help the management team define and improve their approach while developing their teams’ capabilities.
The implementation was divided into three phases:
- Phase 1: Problem Management We determined the management team’s role in site problem-solving and identified nine staff members for training in a Nine Step Problem Solving methodology. A site problem management system was introduced to govern the approach and ensure process confirmation.
- Phase 2: Kata-based Gemba The team was trained and coached in Kata coaching and Improvement Kata, leading to the implementation of these methodologies in the print area. This helped develop critical thinking and was incorporated into a Kata-based morning Gemba walk.
- Phase 3: Learning Through Experimentation The Kata routine coaching plan was further developed to include observations of the management team’s onsite coaching and feedback. We introduced a go-look-see methodology as part of problem-solving, which led to the development of a Kata-based A3 methodology for applying experimentation to improvement projects.
The impact of these new approaches on the facility’s performance was significant. The site achieved £5.3 million in savings through the implementation of the Nine Step problem-solving and Kata coaching.
Examples of these savings include inventory reduction, polymer spoil reduction, ink utilisation, and polymer BPS model adaptation. Additionally, the site realised £1.1 million in cost avoidance through the same methodologies, including mitigation of polymer spoilage and cut registration issues.
This project demonstrated the profound impact that a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving can have on an organisation. By fostering a problem-solving mindset and developing leadership coaching capabilities, the client was able to achieve substantial improvements in performance and efficiency.
At Project7 Consultancy, we remain dedicated to helping our clients achieve their goals through targeted performance improvements and leadership development. Our work on this project underscores the value of practical problem-solving and Kata coaching in driving continuous improvement and achieving lasting results.
Please contact us for more information on how we can assist your organisation in achieving similar success.

